NCLEX Cirrhosis
NCLEX Cirrhosis
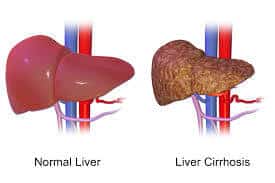
Cirrhosis is a late stage of scarring (fibrosis) of the liver caused by many forms of liver diseases and conditions, such as hepatitis and chronic alcoholism. The liver carries out several necessary functions, including detoxifying harmful substances in your body, cleaning your blood and making vital nutrients.
Decompensated cirrhosis is the term used to describe the development of specific complications resulting from the changes brought on by cirrhosis. Decompensated cirrhosis is life-threatening.
The liver damage done by cirrhosis generally can’t be undone. But if liver cirrhosis is diagnosed early and the cause is treated, further damage can be limited and, rarely, reversed.
Signs and Symptoms
Cirrhosis often has no signs or symptoms until liver damage is extensive. When signs and symptoms do occur, they may include:
- Fatigue
- Bleeding easily
- Bruising easily
- Itchy skin
- Yellow discoloration in the skin and eyes (jaundice)
- Fluid accumulation in your abdomen (ascites)
- Loss of appetite
- Nausea
- Swelling in your legs
- Weight loss
- Confusion, drowsiness and slurred speech (hepatic encephalopathy)
- Spiderlike blood vessels on your skin
- Redness in the palms of the hands
- Testicular atrophy in men
- Breast enlargement in men
Causes
A wide range of diseases and conditions can damage the liver and lead to cirrhosis. The most common causes are:
- Chronic alcohol abuse
- Chronic viral hepatitis (hepatitis B and C)
- Fat accumulating in the liver (nonalcoholic fatty liver disease)
Other possible causes include:
- Iron buildup in the body (hemochromatosis)
- Cystic fibrosis
- Copper accumulated in the liver (Wilson’s disease)
- Poorly formed bile ducts (biliary atresia)
- Inherited disorders of sugar metabolism (galactosemia or glycogen storage disease)
- Genetic digestive disorder (Alagille syndrome)
- Liver disease caused by your body’s immune system (autoimmune hepatitis)
- Destruction of the bile ducts (primary biliary cirrhosis)
- Hardening and scarring of the bile ducts (primary sclerosing cholangitis)
- Infection such schistosomiasis
- Medications such as methotrexate
Complications
- High blood pressure in the veins that supply the liver (portal hypertension).Cirrhosis slows the normal flow of blood through the liver, thus increasing pressure in the vein that brings blood from the intestines and spleen to the liver.
- Swelling in the legs and abdomen. Portal hypertension can cause fluid to accumulate in the legs (edema) and in the abdomen (ascites). Edema and ascites also may result from the inability of the liver to make enough of certain blood proteins, such as albumin.
- Enlargement of the spleen (splenomegaly). Portal hypertension can also cause changes to the spleen. Decreased white blood cells and platelets in your blood can be a sign of cirrhosis with portal hypertension.
- Bleeding. Portal hypertension can cause blood to be redirected to smaller veins, causing them to increase in size and become varices. Strained by the extra load, these smaller veins can burst, causing serious bleeding. Life-threatening bleeding most commonly occurs when veins in the lower esophagus (esophageal varices) or stomach (gastric varices) rupture. If the liver can’t make enough clotting factors, this also can contribute to continued bleeding. Bacterial infections are a frequent trigger for bleeding.
- Infections. If you have cirrhosis, your body may have difficulty fighting infections. Ascites can lead to spontaneous bacterial peritonitis, a serious infection.
- Malnutrition. Cirrhosis may make it more difficult for your body to process nutrients, leading to weakness and weight loss.
- Buildup of toxins in the brain (hepatic encephalopathy). A liver damaged by cirrhosis isn’t able to clear toxins from the blood as well as a healthy liver can. These toxins can then build up in the brain and cause mental confusion and difficulty concentrating. Hepatic encephalopathy symptoms may range from fatigue and mild impairment in cognition to unresponsiveness or coma.
- Jaundice. Jaundice occurs when the diseased liver doesn’t remove enough bilirubin, a blood waste product, from your blood. Jaundice causes yellowing of the skin and whites of the eyes and darkening of urine.
- Bone disease. Some people with cirrhosis lose bone strength and are at greater risk of fractures.
- Increased risk of liver cancer. A large proportion of people who develop liver cancer that forms within the liver itself have cirrhosis.
- Acute-on-chronic liver failure. Some people end up experiencing multiorgan failure. Researchers now believe this is a distinct complication in some people who have cirrhosis, but they don’t fully understand its causes.
Treatments
Treatment for cirrhosis depends on the cause and extent of your liver damage. The goals of treatment are to slow the progression of scar tissue in the liver and to prevent or treat symptoms and complications of cirrhosis.
NCLEX National Exam Courses
Overview
- Elite Reviews Offers A Variety Of Online Courses That Will More Than Adequately Help Prepare The Graduate Nurse To Pass The National Exam.
- Each Course Includes Sample Questions & The Most Current NCLEX Exam Updates.
NCLEX Free Trial
- FREE Sample Lecture & Practice Questions
- Available For 24 Hrs After Registration
- Click The Free Trial Link To Get Started – NCLEX Free Trial
How It Works
How The Course Works
- First – Purchase The Course By Clicking On The Blue Add To Cart Button – You Will Then Be Prompted To Create A User Account.
- Second – After Creating An Account, All 3 Options (90, 120, 150 Days) Will Be Listed. Select The Option You Desire And Delete The Other Two.
- Third – You Will Be Prompted To Pay For This Review Using PayPal – After Payment You Will Be Redirected Back To Your Account.
- Last – Click The Start Button Located Within Your Account To Begin The Course
- 175 Prep Questions
- Q & A With Rationales
- Alt. Format Questions
- 90 Days Availability
- Cost $75.00
- 1250+ Prep Questions
- Q & A With Rationales
- Alt. Format Questions
- 90 Days Availability
- Cost $200.00
NCLEX Practice Questions Bundle
- 1350+ Prep Questions
- Q & A With Rationales
- Alt. Format Questions
- 90 Days Availability
- Cost $225.00
NCLEX Review Course
- Option 1
- Lectures & 1250+ Questions
- Q & A With Rationales
- Alt. Format Questions
- 90 Days Availability
- Cost $275.00
- Option 2
- Lectures & 2000+ Questions
- Q & A With Rationales
- Alt. Format Questions
- 90 Days Availability
- Cost $325.00
NCLEX Review Course Bundle
- Option 3
- Lectures & 3000+ Questions
- Q & A With Rationales
- Alt. Format Questions
- 90 Days Availability
- Cost $375.00