CEN Alzheimers Disease
CEN Alzheimers Disease Overview
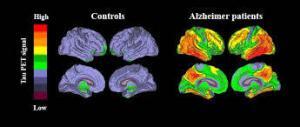
Alzheimer’s disease is a progressive disorder that causes brain cells to waste away (degenerate) and die. Alzheimer’s disease is the most common cause of dementia — a continuous decline in thinking, behavioral and social skills that disrupts a person’s ability to function independently.
The early signs of the disease may be forgetting recent events or conversations. As the disease progresses, a person with Alzheimer’s disease will develop severe memory impairment and lose the ability to carry out everyday tasks.
Current Alzheimer’s disease medications may temporarily improve symptoms or slow the rate of decline. These treatments can sometimes help people with Alzheimer’s disease maximize function and maintain independence for a time. Different programs and services can help support people with Alzheimer’s disease and their caregivers.
There is no treatment that cures Alzheimer’s disease or alters the disease process in the brain. In advanced stages of the disease, complications from severe loss of brain function — such as dehydration, malnutrition or infection — result in death.
Signs and Symptoms
Memory loss is the key symptom of Alzheimer’s disease. An early sign of the disease is usually difficulty remembering recent events or conversations. As the disease progresses, memory impairments worsen and other symptoms develop.
At first, a person with Alzheimer’s disease may be aware of having difficulty with remembering things and organizing thoughts. A family member or friend may be more likely to notice how the symptoms worsen.
Causes
Scientists believe that for most people, Alzheimer’s disease is caused by a combination of genetic, lifestyle and environmental factors that affect the brain over time.
Less than 1 percent of the time, Alzheimer’s is caused by specific genetic changes that virtually guarantee a person will develop the disease. These rare occurrences usually result in disease onset in middle age.
The exact causes of Alzheimer’s disease aren’t fully understood, but at its core are problems with brain proteins that fail to function normally, disrupt the work of brain cells (neurons) and unleash a series of toxic events. Neurons are damaged, lose connections to each other and eventually die.
The damage most often starts in the region of the brain that controls memory, but the process begins years before the first symptoms. The loss of neurons spreads in a somewhat predictable pattern to other regions of the brains. By the late stage of the disease, the brain has shrunk significantly.
Risk Factors
- Age
- Family history and genetics
- Down syndrome
- Sex
- Mild cognitive impairment
- Past head trauma
- Poor sleep patterns
- Lifestyle and heart health
- Lifelong learning and social engagement
Complications
Memory and language loss, impaired judgment, and other cognitive changes caused by Alzheimer’s can complicate treatment for other health conditions. A person with Alzheimer’s disease may not be able to:
- Communicate that he or she is experiencing pain — for example, from a dental problem
- Report symptoms of another illness
- Follow a prescribed treatment plan
- Notice or describe medication side effects
As Alzheimer’s disease progresses to its last stages, brain changes begin to affect physical functions, such as swallowing, balance, and bowel and bladder control. These effects can increase vulnerability to additional health problems such as:
- Inhaling food or liquid into the lungs (aspiration)
- Pneumonia and other infections
- Falls
- Fractures
- Bedsores
- Malnutrition or dehydration
Prevention
- Exercise regularly
- Eat a diet of fresh produce, healthy oils and foods low in saturated fat
- Follow treatment guidelines to manage high blood pressure, diabetes and high cholesterol
- If you smoke, ask your doctor for help to quit smoking
Treatment
Current Alzheimer’s medications can help for a time with memory symptoms and other cognitive changes. Two types of drugs are currently used to treat cognitive symptoms:
- Cholinesterase inhibitors. These drugs work by boosting levels of cell-to-cell communication by preserving a chemical messenger that is depleted in the brain by Alzheimer’s disease. The improvement is modest.Cholinesterase inhibitors may also improve neuropsychiatric symptoms, such as agitation or depression. Commonly prescribed cholinesterase inhibitors include donepezil (Aricept), galantamine (Razadyne) and rivastigmine (Exelon).The main side effects of these drugs include diarrhea, nausea, loss of appetite and sleep disturbances. In people with cardiac conduction disorders, serious side effects may include cardiac arrhythmia.
- Memantine (Namenda). This drug works in another brain cell communication network and slows the progression of symptoms with moderate to severe Alzheimer’s disease. It’s sometimes used in combination with a cholinesterase inhibitor. Relatively rare side effects include dizziness and confusion.
Emergency Room Certification Courses
Overview
- Elite Reviews Offers A Variety Of Online Courses That Will More Than Adequately Help Prepare The Emergency Nurse To Pass The National Exam.
- Each Course Includes Continuing Education Credit and Sample Questions.
Continuing Education
- Each Of Our Online Courses Has Been Approved Continuing Education Contact Hours by the California Board of Nursing
- Login To Your Account In Order To Access The Course Completion Certificate Once The Course Is Complete.
CEN Free Trial
- FREE Sample Lecture & Practice Questions
- Available For 24 Hrs After Registration
- Click Free Trial Link To Get Started – CEN Free Trial
How It Works
How The Course Works
- First – Purchase The Course By Clicking On The Blue Add To Cart Button – You Will Then Be Prompted To Create A User Account.
- Second – After Creating An Account, All 3 Options (90, 120 or 150 Days) Will Be Listed. Select The Option You Desire And Delete The Other Two.
- Third – You Will Be Prompted To Pay For The Review Using PayPal – After Payment You Will Be Redirected Back To Your Account.
- Last – Click The Start Button Located Within Your Account To Begin The Program
- 175 Sample Questions
- Q & A With Rationales
- Approved For 5 CEU’s
- 90 Days Availability
- Cost $75.00
- 1250+ Sample Questions
- Q & A With Rationales
- Approved For 25 CEU’s
- 90 Days Availability
- Cost $200.00
CEN Practice Questions Bundle
- 1350+ Sample Questions
- Q & A With Rationales
- Approved For 30 CEU’s
- 90 Days Availability
- Cost $225.00
CEN Review Course
- Option 1
- Lectures & 1250+ Questions
- Approved For 35 CEU’s
- 90 Days Availability
- Cost $325.00
- Option 2
- Lectures & 2000+ Questions
- Approved For 40 CEU’s
- 90 Days Availability
- Cost $350.00
CEN Review Course Bundle
- Option 3
- Lectures & 3000+ Questions
- Approved For 70 CEU’s
- 90 Days Availability
- Cost $375.00